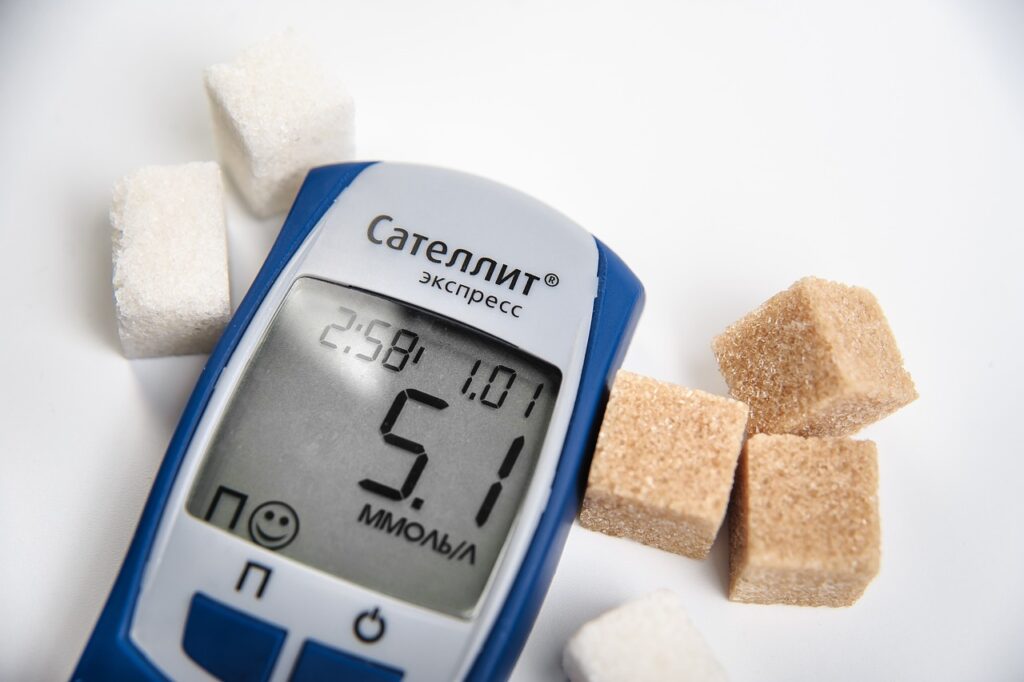
It is a long-term condition that arises when the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin or when the body cannot properly utilize the insulin that is produced. Insulin is a hormone responsible for controlling blood sugar levels.
Blog Contents
Diabetes Population in World:
The worldwide population affected by it has significantly rising, increasing from 200 million in 1990 to 830 million by 2022. This increasing prevalence is particularly evident in low- and middle-income countries, where the rates are more swiftly than in high-income countries. Alarmingly, in 2022, more than half of the individuals diagnosed with diabetes did not receive any form of treatment, with the most limited treatment access found in low- and middle-income regions. It can result in serious health issues, such as vision impairment, kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, and lower limb amputations. In 2021, diabetes and related kidney conditions accounted for over 2 million deaths, with around 11% of cardiovascular deaths attributed to raised in blood glucose levels. Effective management of diabetes through appropriate treatment is essential to avoid these potentially fatal complications.

The Hidden Symptoms and Causes
- experiencing extreme thirst
- unclear vision
- tiredness
- weight loss
- sores or cuts.
- Skin infections
- Dry Mouth

Among the many obvious symptoms are extreme thirst, loss of vision, tiredness, and unexplainable weight loss. Furthermore, people with diabetes may slow healing cuts or sores. It frequently results in these delayed healing times as well as an increased risk of skin infections. Blood sugar imbalances the body’s defenses against infections, especially those that affect the skin, by weakening the immune system. Effective diabetes management is essential to avoiding these issues and preserving general health.
Types and causes of Diabetes:
When your body is unable to sufficiently control blood sugar (glucose),it results. Depending on the type of it, there are different causes of rising blood sugar:
1. Cause of Type 1
The immune system of the body targets the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, causing the production of insulin to completely stop. Blood sugar levels cannot be regulated without insulin.
Factors Environmental triggers such as viruses and genetics may be involved.
2. Type 2
The body develops resistance to insulin in Type 2 diabetes, which results in improper cell response to the hormone. The body consequently produces more insulin, but it is unable to keep up. This eventually results in high levels of sugar.
Factors include having a poor diet, not exercising enough, being overweight, and family history all increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
3. Gestational
Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia with blood glucose values above normal but below those diagnostic. It occurs during pregnancy.
Women with it are at an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and at delivery. These women and possibly their children are also at increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the future.
In short, it is caused when the body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it properly, leading to high blood sugar levels. It can develop as a result of lifestyle choices, genetics, and other medical conditions.
Prevention
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or its onset postponed by maintaining a normal body weight, avoiding tobacco use, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity. Diet, exercise, medication, and routine screening and treatment for complications can all help prevent or delay the consequences.
Adopting a number of healthy lifestyle practices is crucial to lowering the risk of developing diabetes. Begin by eating a healthy diet that endorses balanced eating, like the Mediterranean diet, which can help manage blood sugar levels. It’s also crucial to incorporate regular exercise into your schedule; try to get in at least 30 minutes of physical activity five days a week. You can further reduce your risk of diabetes by achieving and maintaining a healthy weight that suits you. Stress management is essential, so practice stress-reduction strategies to help regulate blood sugar levels. Reducing alcohol consumption may also help control blood sugar and lower the risk of diabetes. Additionally, it’s critical to get 7 to 9 hours of good sleep each night.

[…] Also read our previous blog. […]
[…] ALSO READ: Diabetes: 7 key Symptoms, causes, and Powerful Prevention […]