
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It can lead to mild to severe symptoms and, in some cases, serious complications. Understanding the flu, its prevention, and treatment options can help reduce its impact.
What is Influenza?
Influenza is an infectious disease that primarily affects the nose, throat, and lungs. It spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. The flu is seasonal, with outbreaks typically occurring in fall and winter.
Common Symptoms of Influenza
Symptoms usually appear 1 to 4 days after infection and may include:
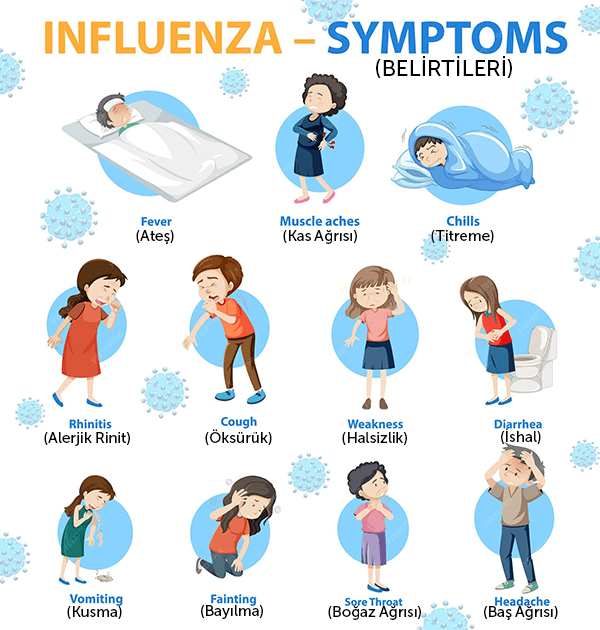
- Fever or chills
- Cough and sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Muscle or body aches
- Fatigue (tiredness)
- Headache
- Shortness of breath
- Vomiting or diarrhea (more common in children)
Causes and Risk Factors

Influenza is caused by influenza A, B, C, and D viruses, with types A and B being the most common causes of seasonal flu outbreaks. Risk factors for severe illness include:
- Weakened immune systems
- Chronic conditions (e.g., asthma, diabetes, heart disease)
- Pregnancy
- Young children and older adults
- Healthcare workers
How to Prevent Influenza
Preventing the flu is crucial for maintaining public health. Effective prevention measures include:
1. Annual Flu Vaccination
Getting a flu shot each year helps protect against the most prevalent influenza strains.
2. Good Hygiene Practices
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water.
- Cover mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid touching the face with unwashed hands.
3. Boosting Immunity
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins.
- Get regular exercise and adequate sleep.
- Manage stress effectively.
4. Avoiding Contact with Sick Individuals
Minimizing exposure to infected individuals can reduce the risk of catching the flu.
Treatment Options for Influenza
While most cases of influenza resolve on their own, treatment can help relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
Home Remedies
- Rest to allow the body to recover.
- Stay hydrated with water, herbal tea, or electrolyte drinks.
- Use a humidifier to ease congestion.
Over-the-Counter Medications
- Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen for fever and body aches.
- Decongestants and cough suppressants to relieve symptoms.
Antiviral Drugs
In severe cases, antiviral medications like oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza) can reduce flu severity and duration when taken within 48 hours of symptom onset.
Complications of Influenza
Severe flu cases can lead to serious complications, including:
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Sinus infections
- Worsening of chronic conditions (e.g., asthma, heart disease)
Final Thoughts
Influenza is a highly contagious disease that can be prevented with vaccines, good hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle. Understanding the symptoms and available treatments ensures better management of the flu season.
Stay Informed, Stay Healthy!
If you experience severe flu symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately to prevent complications.
Also Read: The Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV): What You Need to Know
